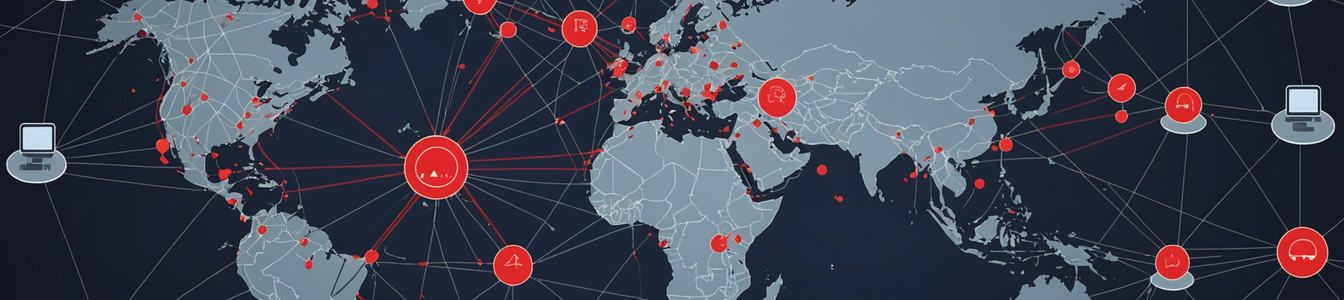
The cybersecurity landscape is witnessing a dramatic resurgence of sophisticated botnet campaigns that are systematically targeting vulnerable PHP servers and Internet of Things (IoT) devices across global networks. Security researchers have documented an alarming spike in automated attacks that leverage known vulnerabilities in web infrastructure, creating massive botnets capable of launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, data exfiltration, and credential harvesting operations.
These campaigns demonstrate unprecedented levels of automation, enabling threat actors to scan, identify, and exploit vulnerable systems at scale. The attacks primarily target unpatched PHP servers running outdated versions or misconfigured web applications, alongside poorly secured IoT devices including routers, cameras, and smart home equipment. The convergence of these attack vectors creates a perfect storm for enterprise security teams struggling to maintain comprehensive visibility across their digital infrastructure.
Technical analysis reveals that these botnets employ sophisticated scanning techniques to identify potential targets, followed by automated exploitation of Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) that have available public exploits. The attackers particularly focus on vulnerabilities in popular PHP frameworks, content management systems, and IoT device management interfaces that often lack proper security hardening.
Network security professionals emphasize that traditional firewall configurations alone are insufficient to counter these advanced threats. Modern botnets can bypass basic security measures by mimicking legitimate traffic patterns and using encrypted communication channels. The evolving tactics include dynamic command-and-control infrastructure that rotates through multiple domains and IP addresses, making detection and takedown operations significantly more challenging.
Critical security measures recommended by experts include implementing robust web application firewalls (WAFs), conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and establishing comprehensive patch management processes. Organizations must also deploy advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying anomalous network behavior and suspicious traffic patterns indicative of botnet activity.
The IoT security aspect presents particular challenges, as many connected devices lack built-in security features and cannot be easily updated or patched. Security teams should implement network segmentation to isolate IoT devices from critical business systems and deploy specialized monitoring solutions for IoT network traffic.
Cloud infrastructure has become another prime target, with attackers exploiting misconfigured cloud instances and containerized applications. The shared responsibility model in cloud environments requires both providers and customers to maintain vigilant security postures, including proper access controls, encryption, and continuous monitoring.
Looking forward, the cybersecurity community anticipates further evolution in botnet capabilities, including the integration of artificial intelligence for more sophisticated target selection and evasion techniques. Proactive defense strategies must adapt accordingly, incorporating behavioral analysis, machine learning detection systems, and coordinated threat intelligence sharing across the industry.
Organizations are advised to develop comprehensive incident response plans specifically addressing botnet infections, including procedures for isolating compromised systems, conducting forensic analysis, and implementing remediation measures. Regular security awareness training for IT staff remains crucial for maintaining effective defense postures against these evolving automated threats.
Comentarios 0
Comentando como:
¡Únete a la conversación!
Sé el primero en compartir tu opinión sobre este artículo.
¡Inicia la conversación!
Sé el primero en comentar este artículo.